Emphysematous pyelonephritis (EPN) is a severe necrotizing infection of the renal parenchyma, with formation of gas within the collecting system, renal parenchyma, or perirenal tissues. Gas in the renal pelvis alone, without parenchymal gas, is often referred to as emphysematous pyelitis. EPN is common in persons with diabetes, and presentation is similar to acute pyelonephritis. However, the clinical course can be severe and life-threatening if not recognized and treated promptly.
Among the bacteria identified in patients with EPN, Escherichia coli is isolated in 66% of patients and Klebsiella species are reported in 26%. Proteus, Pseudomonas, and Streptococcus species are other organisms found in patients with EPN. Mixed organisms are observed in 10%. Positive blood culture results are identical to urine culture results in 54%. Rare organisms, such as Clostridium and Candida species, have also been isolated in patients with EPN. Recently, Entamoeba histolytica and Aspergillus fumigatus have been reported as causes of EPN.
EPN is a severe infection of the renal parenchyma, with the accumulation of gas in the tissues. The infection often has a fulminating course and can be fatal if left untreated. Yet, urinary tract infections are very common in patients with diabetes, and not all of these infections lead to EPN. The factors that predispose to EPN in persons with diabetes are thought to be uncontrolled diabetes, high levels of glycosylated hemoglobin, and impaired host immune mechanisms
Kidneys, ureter, bladder imaging often reveals gas distribution over the region of the kidneys. In patients with emphysematous pyelitis, the collecting system may be filled with gas. An ileus pattern may be seen, suggesting retroperitoneal inflammation.
Imaging features
Imaging features
Renal ultrasound images often reveal high echogenic areas with dirty shadowing. Hydronephrosis and perinephric fluid may also be seen.
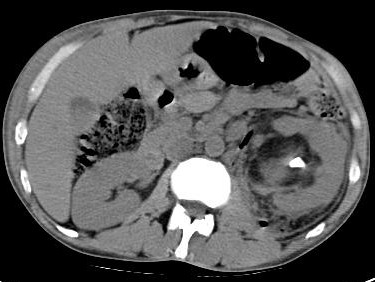
CT scan is the definitive test. Several patterns have been described, including streaky, streaky and mottled, and streaky and bubbly. Gas can be rim like or crescent-shaped in the perinephric area. Gas can also be seen in the renal vein or inferior vena cava. Gas can be seen along the psoas muscle. Perinephric abscess may also lead to significant gas in the perinephric space. A stone may be seen in the collecting system
Staging by Huang et al
Class 1 - Gas confined to the collecting system
Class 2 - Gas confined to the renal parenchyma alone
Class 3A - Perinephric extension of gas or abscess
Class 3B - Extension of gas beyond the Gerota fascia
Class 4 - Bilateral EPN or EPN in solitary kidney