The term, velum, derived from Latin velum, meaning a \"sail\", \"curtain,\" \"awning\" or \"veil\",
The velum interpositum is located in the roof of the third ventricle below the body of the fornix. The upper and lower walls of the velum interpositum are formed by two membranous layers of tela choroidea in the roof of the third ventricle. The layer that is attached to the lower surface of the fornix and hippocampal commissars forms the upper wall. The lower wall is attached to the superior surface of the pineal body and tectum posteriorly
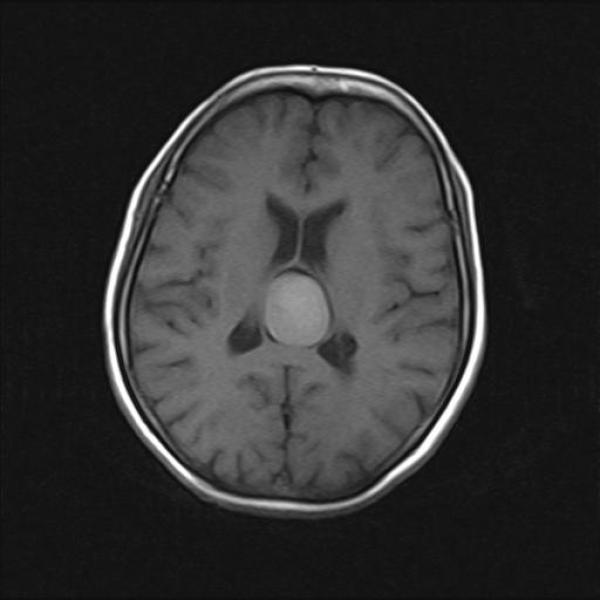
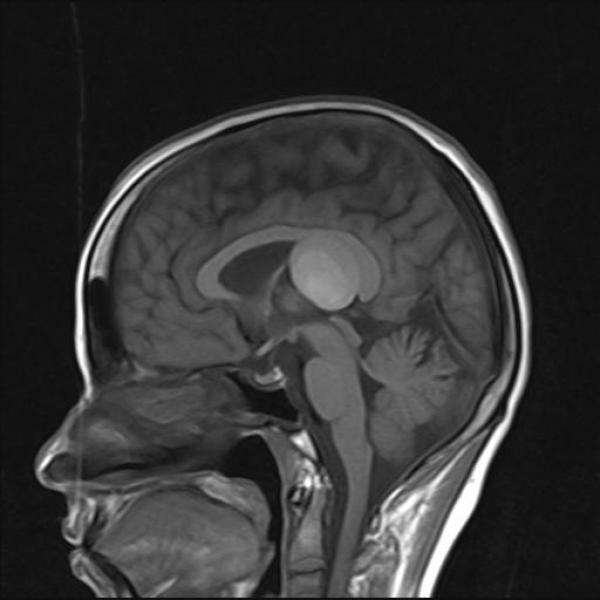
The lesion is colloid cyst . The term colloid cyst refers to only neuroepithelial cysts that arise in the anterosuperior third ventricle, near the foramina of Monro.However, rare reports describe cysts in other locations in this case it is velum interpositum.
On CT colloid cysts appear homogenous, with two thirds of them appearing hyperdense to the surrounding parenchyma and one third appearing isodense to the surrounding parenchyma. The lesions are well delineated and are usually round or ovoid.
The MRI signal intensity of colloid cysts is notoriously variable, with any combination of T1- and T2-signal intensities described. The most common appearance is hyperintensity with T1-weighted sequences and isointensity to hypointensity with T2 sequences. Recognizing that a CSF flow artifact at the Monro foramen can mimic the appearance of a colloid cyst through MRI is important. Finally, the Constructive Interference in the Steady State (CISS) sequence of a MRI can delineate an abnormal contour of the ventricular system and intraventricular septa, from which essential information for surgical planning, including endoscopic surgery can be obtained
OTHER LESIONS AT VELUM INTERPOSITUM
Numerous cysts and cyst-like anatomic variants have been located in the velum interpositum . These include physiologic enlargement and cyst of the cavum velum interpositum . Other lesions occurring at this site include meningiomas and pinealoblastomas/pinealocytomas (which are solid) and cystic lesions like arachnoid cysts and epidermoid cysts.
a] The CSP is the potential space which develops between the two leaflets of the septum pellucidum.
b] Cavum Vergae (CV)
It is called the sixth ventricle. It is bounded superiorly
by the body of the corpus callosum, inferiorly by the
hippocampal commissure, laterally by the crus of the
fornix, and posteriorly by the splenium of the corpus
callosum
c] CVI is a fusion defect of the velum interpositum found in the roof of the third ventricle.